For Professionals, By Professionals

Discover ProX PC for best custom-built PCs, powerful workstations, and GPU servers in India. Perfect for creators, professionals, and businesses. Shop now!
SERVICES
WE ACCEPT








Contents
This article provides a guide to Edge Computing in 2021. Recently, industry investment and research interest in Edge Computing have grown dramatically. Computing at the Edge moves computing and storage from the Cloud to the Internet’s edge in close proximity to mobile devices or sensors.
Hence, Edge Computing makes it possible to deliver highly responsive services for mobile computing, scalability, and privacy-policy enforcement of Big-data-based AI processing at the Edge. Explore ProX micro edge devices at proxpc.com
In the following, we will provide an easy-to-understand guide covering the following topics:
About us: ProX PC is the premier computer vision infrastructure for enterprises. With the entire ML pipeline under one roof, ProX PC eliminates the need for point solutions. To learn more about how ProX PC can help automate your business needs, book a demo with our team.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a new paradigm that performs computing at the edge of the network. As opposed to cloud computing, edge computing moves closer to the user and closer to the source of data. At the edge of the network, it is lightweight for local, small-scale data storage and processing.
With the rapid development of the Internet of Everything (IoE), the number of smart devices connected to the Internet is growing fast, generating large-scale data (Big Data) at the network edge. The massive amount of data causes problems such as bandwidth load, slow response speed, poor security, and poor privacy in traditional cloud computing models.

Today’s mass connectivity requires faster and higher-quality computing
Hence, traditional cloud computing is no longer sufficient to support today’s requirements for smart services and intelligent data processing, so edge computing technologies have emerged.
Edge computing directs computational data, applications, and services away from cloud servers to the edge of a network. As a result, application developers can use the on-device computing systems by offering the users services closer to them. Edge computing is characterized in terms of high bandwidth, ultra-low latency, and real-time access to network information that can be used by several applications.
Therefore, edge computing is the foundation of next-generation Edge Intelligence, the deployment of machine learning algorithms to the edge device where the data is generated.
Edge Computing Definition
Since edge computing work has become a research hotspot, there are different definitions. Satyanarayanan, a professor at Carnegie Mellon University, defines Edge Computing as “a new computing model that deploys computing and storage resources (such as cloudlets, micro data centers, or fog nodes, etc.) at the edge of the network closer to mobile devices or sensors.”
China’s Edge Computing Consortium defines Edge Computing as “near the edge of the network or the source of the data, an open platform that integrates core capabilities such as networking, computing, storage, applications, and provides edge intelligent services nearby to meet the industry agility key requirements in connection, real-time business, data optimization, application intelligence, security, and privacy.”
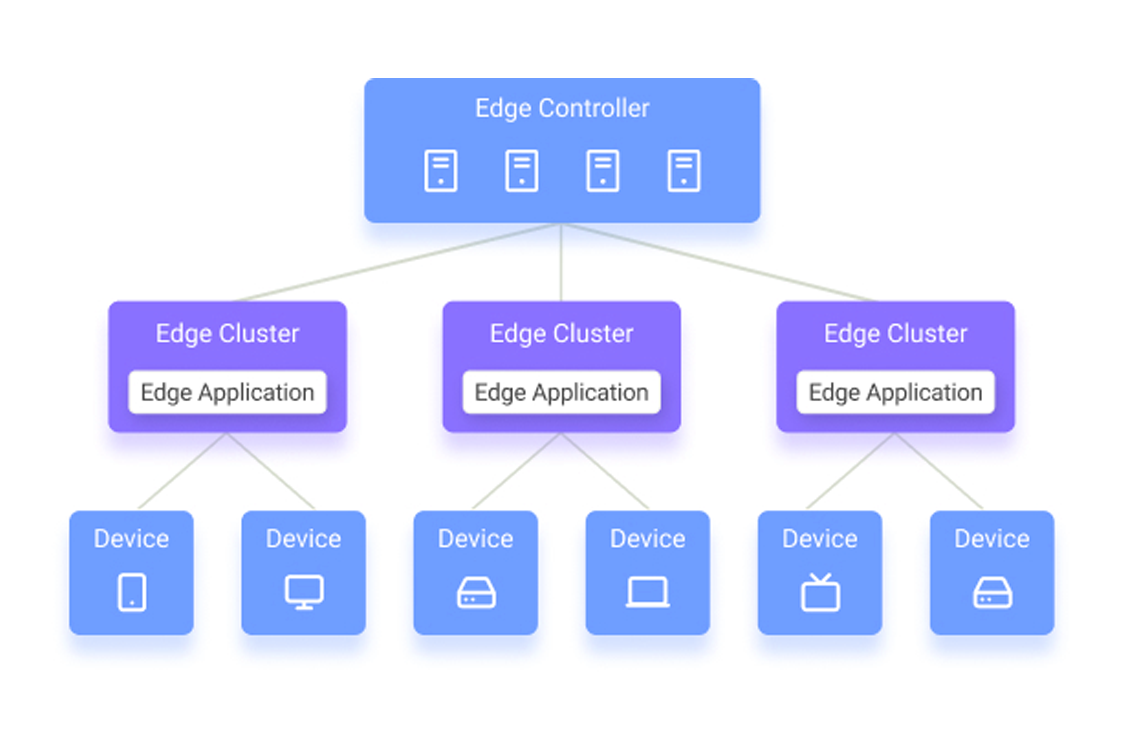
Concept of Edge Computing and Edge Devices
Zha provides the following definition: “Edge computing is a new computing model that unifies resources that are close to the user in geographical distance or network distance to provide computing, storage, and network for applications service.”
Background and Need For Computing at the Edge
Today’s intelligent society is driven by the need for smart and connected services across various industries. Edge devices have spread to all aspects of society, such as smart homes, surveillance cameras, autonomous vehicles, intelligent production robots, and more. As a result, the number of connected devices is constantly increasing.
Therefore, the amount of data generated by devices worldwide is drastically increasing. Based on the continuous and massive growth of the volume of data and various data processing requirements, cloud-based big data processing has shown many shortcomings:
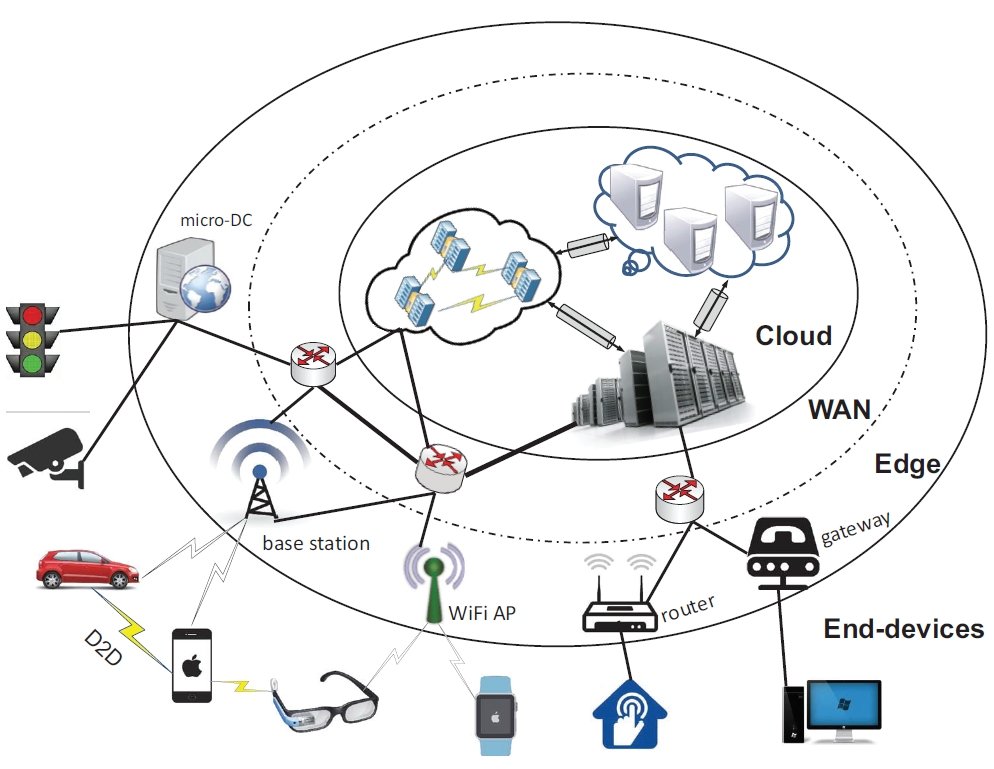
Connectivity and the need for edge computing
Therefore, edge computing technology aims to provide services and perform computations at the edge of the network and data generation. The goal of edge computing is to migrate the cloud’s network, computing, storage capabilities, and resources to the edge of the network and provide intelligent services.
This is required to meet the critical needs of the IT industry in real-time business, application intelligence, data optimization, security, and privacy, and to meet the requirements of low latency and high bandwidth on the network.
Differences of Edge vs. Cloud Computing
Traditional cloud computing transfers all data to the cloud computing center through the network and solves the computing and storage problems in a centralized way. However, the emergence of edge computing will not replace cloud computing.
The two concepts complement each other, enabling the digital transformation of industries to a greater extent. Edge is an advanced version of cloud computing that reduces latency by bringing the services close to the end users. In addition, it minimizes the load of the cloud by providing resources and services in the Edge network.
In some Internet services, some data needs to be returned to the cloud for processing after being processed by edge computing, such as in-depth analysis of data mining and sharing, which requires the cooperation of both concepts.
The main differences between cloud and edge computing are the following:
At this time, edge computing is required to share the pressure of the cloud and take charge of tasks within its scope of the edge. In addition, local data processing reduces the risk of large-scale data loss. Those factors bring stability to services that include connected devices in a network (IoT).
What is Fog Computing?
Fog Computing was introduced by CISCO in 2012 and was defined as “a highly virtualized platform that provides compute, storage, and networking services between end devices and traditional cloud computing Data Centers, typically, but not exclusively located at the edge of the network.”
The OpenFog Consortium definition of Fog Computing is “a system-level horizontal architecture that distributes resources and services of computing, storage, control, and networking anywhere along the continuum from Cloud to Things, thereby accelerating the velocity of decision-making.”
Hence, Fog Computing is a concept where a huge number of heterogeneous, ubiquitous, and geographically distributed devices communicate with the network to perform storage and processing tasks without the intervention of third parties. These tasks can support basic network functions or new services and applications that run in an isolated environment.
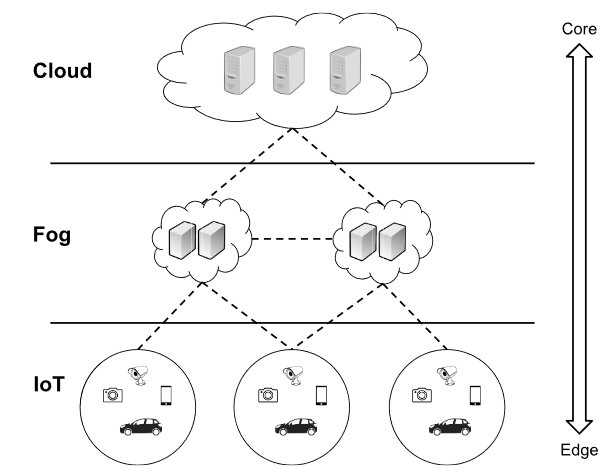
Concept of Fog Computing
Edge Computing Characteristics
Edge computing possesses several characteristics similar to cloud computing but extends the cloud by its specific architecture:
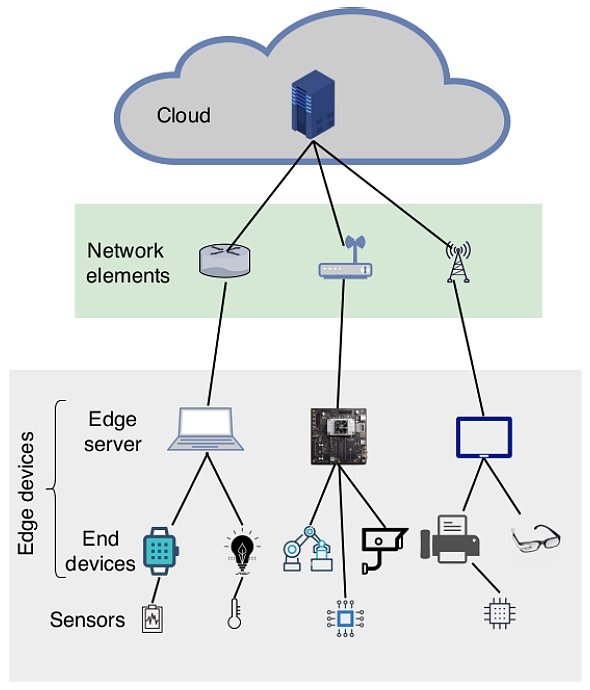
General overview of the edge computing architecture
Benefits of Edge Computing
Edge computing systems store and process data collected locally on devices without uploading it to a cloud computing platform. This comes with several important advantages to lowering the pressure of network bandwidth and other disadvantages of cloud computing.
Edge Computing Use Cases

For more info visit www.proxpc.com
Related Products


Share this: