Maximizing Deep Learning Performance on NVIDIA Jetson Orin with DLA
Introduction
Deep learning has revolutionized various fields, from computer vision to natural language processing. However, deploying deep learning models efficiently on edge devices remains challenging. NVIDIA's Jetson Orin, a powerful edge AI platform, addresses this challenge with its Deep Learning Accelerator (DLA). In this blog, we will explore how to maximize the performance of deep learning models on the NVIDIA Jetson Orin using DLA.
Understanding Jetson Orin

Jetson Orin
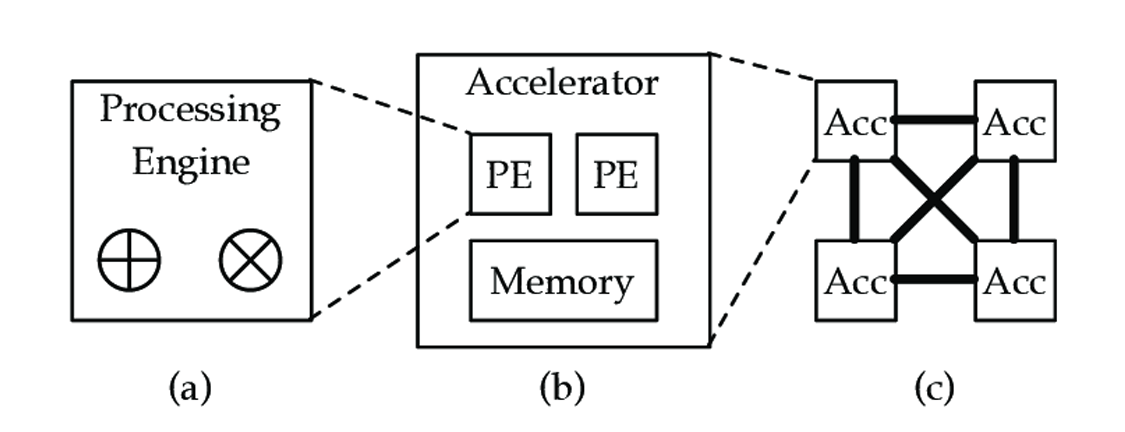
The NVIDIA Jetson Orin is a system-on-module (SoM) designed for edge AI applications. It features a powerful GPU, a high-performance CPU, and dedicated accelerators for deep learning. The key components of Jetson Orin include:
- GPU: The GPU on Jetson Orin is based on the NVIDIA Ampere architecture, providing significant computational power for AI workloads.
- CPU: A multi-core ARM CPU handles general-purpose computing tasks.
- DLA: The Deep Learning Accelerator (DLA) is a specialized hardware component optimized for deep learning inference.
What is DLA?
The DLA on Jetson Orin is designed to accelerate the inference of deep learning models. It offloads computation-intensive tasks from the GPU and CPU, freeing them for other tasks. The DLA is optimized for power efficiency, making it ideal for edge applications where power consumption is critical.
Benefits of Using DLA
- Power Efficiency: The DLA consumes less power compared to the GPU, making it suitable for battery-powered devices.
- Performance: By offloading inference tasks to the DLA, the GPU and CPU can handle other tasks, improving overall system performance.
- Specialization: The DLA is designed specifically for deep learning inference, providing optimized performance for these tasks.
Preparing Your Environment

Preparing Your Environment
To maximize the performance of deep learning models on Jetson Orin, you need to set up your development environment. Here are the steps to get started:
- Install JetPack: JetPack is NVIDIA's SDK for Jetson devices. It includes all necessary libraries and tools for development. You can download JetPack from the NVIDIA website and follow the installation instructions.
- Set Up TensorRT: TensorRT is NVIDIA's high-performance deep learning inference library. It optimizes and accelerates deep learning models for deployment. TensorRT is included in JetPack, but you need to ensure it is set up correctly.
- Install PyTorch or TensorFlow: Depending on your preference, install either PyTorch or TensorFlow. Both frameworks are supported on Jetson Orin and can be used to train and deploy models.
Optimizing Models for DLA
Optimizing Models for DLA
To maximize the performance of your deep learning models on Jetson Orin, you need to optimize them for the DLA. Here are some key steps to follow:
1. Choose the Right Model
Not all models are compatible with the DLA. The DLA supports a subset of operations and layers commonly used in deep learning models. Before optimizing your model, ensure it is compatible with the DLA. NVIDIA provides a list of supported layers and operations in the DLA documentation.
2. Convert the Model to ONNX
ONNX (Open Neural Network Exchange) is an open format for representing deep learning models. It allows models trained in different frameworks to be used with various tools and hardware. To use the DLA, you need to convert your model to the ONNX format. Both PyTorch and TensorFlow provide utilities for exporting models to ONNX.
3. Optimize with TensorRT
TensorRT optimizes deep learning models for deployment on NVIDIA hardware. After converting your model to ONNX, use TensorRT to optimize it for the DLA. TensorRT provides a Python API for this purpose. Here is an example of how to optimize a model with TensorRT:
|
import tensorrt as trt # Load the ONNX model # Create a TensorRT logger and builder # Create a network definition # Parse the ONNX model # Optimize the network for the DLA # Build the TensorRT engine |
4. Deploy the Model
Once the model is optimized with TensorRT, it is ready for deployment on Jetson Orin. Use the TensorRT engine to perform inference. Here is an example of how to run inference with the TensorRT engine:
|
# Allocate memory for input and output # Create a CUDA stream # Run inference # Copy the output from device to host print("Inference output:", output) |
Best Practices for DLA Optimization
- Quantization: Quantize your model to INT8 precision to take advantage of the DLA's optimized INT8 inference capabilities. Quantization reduces the model size and improves inference speed without significantly impacting accuracy.
- Layer Fusion: Fuse compatible layers to reduce memory access overhead and improve computational efficiency. TensorRT automatically performs layer fusion during optimization.
- Batch Size: Choose an appropriate batch size for your application. The DLA is optimized for batch sizes of 1, but larger batch sizes can improve throughput for some models.
- Profile the Model: Use TensorRT's profiling tools to identify bottlenecks in your model and optimize accordingly. Profiling helps you understand how different layers perform on the DLA and make informed optimization decisions.
Real-World Applications
To demonstrate the benefits of using the DLA on Jetson Orin, let's look at a few real-world applications:
1. Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles require real-time perception to navigate safely. By offloading deep learning inference to the DLA, the GPU and CPU can focus on other critical tasks like sensor fusion and path planning. This improves the overall performance and responsiveness of the autonomous system.
2. Robotics
Robots use deep learning for object detection, recognition, and manipulation. The DLA enables efficient inference, allowing robots to operate with lower power consumption and extended battery life. This is crucial for applications like warehouse automation and delivery robots.
3. Healthcare
In healthcare, deep learning models are used for medical imaging, diagnostics, and patient monitoring. The DLA accelerates inference, enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses. This improves patient outcomes and reduces the workload on healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
Maximizing deep learning performance on NVIDIA Jetson Orin with DLA involves understanding the hardware, optimizing models, and following best practices. By leveraging the DLA, you can achieve efficient and high-performance deep learning inference on edge devices. Whether you're working on autonomous vehicles, robotics, or healthcare applications, the Jetson Orin with DLA provides the tools you need to succeed.
For more info visit www.proxpc.com
Edge Computing Products
ProX Micro Edge Orin Developer Kit
Learn More

ProX Micro Edge Orin NX
Learn More

ProX Micro Edge Orin Nano
Learn More

ProX Micro Edge AGX Orin
Share this: