For Professionals, By Professionals

Discover ProX PC for best custom-built PCs, powerful workstations, and GPU servers in India. Perfect for creators, professionals, and businesses. Shop now!
SERVICES
WE ACCEPT








Introduction:
Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a groundbreaking technology that enables computers to create new content, images, music, and even text that mimic human creativity. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the world of generative AI, exploring its underlying principles, innovative applications, and the exciting possibilities it holds for the future. Presented in simple terms, this blog aims to demystify generative AI for beginners and enthusiasts alike.
Understanding Generative AI:
Generative AI refers to a class of algorithms that can generate new content, often indistinguishable from human-created content, based on patterns learned from existing data. Unlike traditional AI models that focus on recognizing patterns or making predictions, generative AI models are capable of generating original output, whether it's images, music, text, or even entire virtual worlds. These models are trained on large datasets and learn to capture the underlying characteristics and structure of the data, allowing them to produce realistic and diverse outputs.

Key Techniques in Generative AI:
Several techniques are commonly used in generative AI, each with its unique approach to creating new content:

1. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): GANs consist of two neural networks – a generator and a discriminator – that are trained in a competitive manner. The generator creates new samples, while the discriminator evaluates their authenticity. Through this adversarial process, GANs learn to generate increasingly realistic output.
2. Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): VAEs are probabilistic models that learn to encode input data into a low-dimensional latent space and decode it back to generate new samples. By sampling from the latent space, VAEs can produce diverse and realistic outputs while preserving the underlying structure of the data.
3. Transformers: Transformers are a type of neural network architecture commonly used in natural language processing tasks. They excel at capturing long-range dependencies in sequential data and have been adapted for generative tasks such as language modeling and text generation.
Applications of Generative AI:
Generative AI has a wide range of applications across various domains, including:

1. Image Generation: Generative models such as GANs can create high-resolution images of human faces, animals, landscapes, and even abstract art.
2. Text Generation: Language models trained on large text corpora can generate coherent and contextually relevant text, ranging from articles and stories to poetry and dialogue.
3. Music Composition: Generative models can compose original music pieces in various genres and styles, mimicking the creativity of human composers.
4. Video Synthesis: GANs can generate realistic videos by predicting future frames based on existing ones, enabling applications such as video inpainting and deepfake generation.
5. Virtual Worlds: Generative AI can create immersive virtual environments, characters, and landscapes for gaming, simulation, and virtual reality applications.
Future Possibilities and Challenges:
The future of generative AI holds boundless possibilities, from advancing creative industries to transforming how we interact with technology and entertainment. However, several challenges must be addressed to realize its full potential:

1. Ethical Considerations: Generative AI raises ethical concerns related to copyright infringement, misinformation, and the misuse of synthetic content for malicious purposes.
2. Bias and Diversity: Generative models may exhibit biases present in the training data, leading to underrepresentation or misrepresentation of certain groups or perspectives.
3. Control and Interpretability: As generative AI becomes more sophisticated, ensuring control and interpretability of the generated output becomes increasingly challenging, raising concerns about accountability and trustworthiness.
Conclusion:
Generative Artificial Intelligence represents a paradigm shift in AI research and technology, unlocking new frontiers in creativity, innovation, and human-computer interaction. In this guide, we've explored the fundamentals of generative AI, including its key techniques, applications, and future possibilities. As we continue to explore the capabilities and challenges of generative AI, let us approach its development and deployment with careful consideration of ethical, societal, and technical considerations. By harnessing the power of generative AI responsibly, we can create a future where artificial intelligence enriches human creativity and enhances our collective imagination.
For more info visit www.proxpc.com
Edge Computing Products
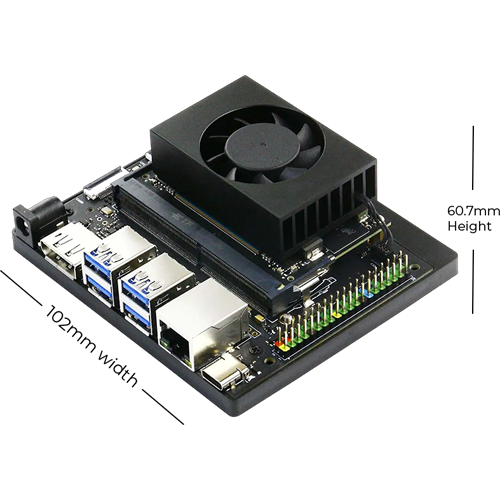
ProX Micro Edge Orin Developer Kit
Learn More
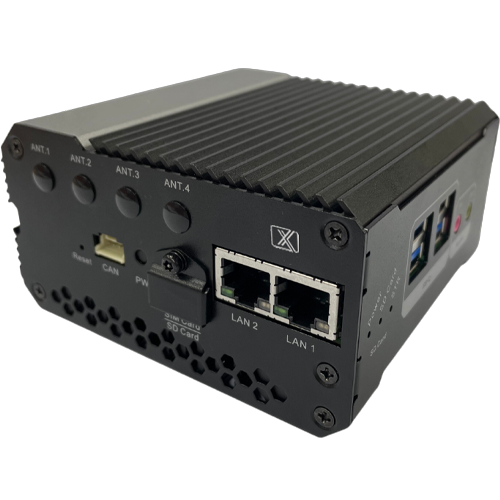

ProX Micro Edge Orin NX
Learn More
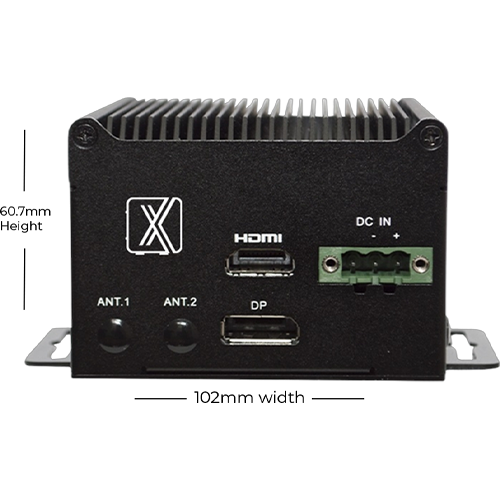

ProX Micro Edge Orin Nano
Learn More
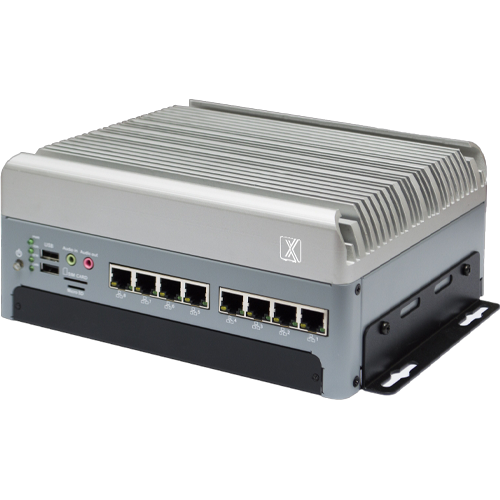

ProX Micro Edge AGX Orin
Share this: