For Professionals, By Professionals

Discover ProX PC for best custom-built PCs, powerful workstations, and GPU servers in India. Perfect for creators, professionals, and businesses. Shop now!
SERVICES
WE ACCEPT








Contents
Edge computing is a crucial aspect of computer vision that allows for data processing to occur at the edge of a network, rather than in the cloud or a data center. This technology is becoming increasingly important as the demand for real-time processing and low-latency applications grows.
In this article, we explore the benefits and applications of edge computing in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and computer vision. Particularly, we will cover:
About us: ProX PC provides the leading end-to-end Computer Vision Platform. Our technology automates edge computing infrastructure to build and scale computer vision applications. Get a demo for your company.
Distributed Computing
Edge computing is essential to computer vision processes for bandwidth, speed, and security purposes. Edge computing tends to be a more efficient, more secure option for data processing related to computer vision.
Although most data processing can happen at the edge, we send data to the cloud for further analysis (partial data offloading). In addition, data sent back to the cloud can be aggregated and used for business analytics tasks.
What Is Edge Computing?
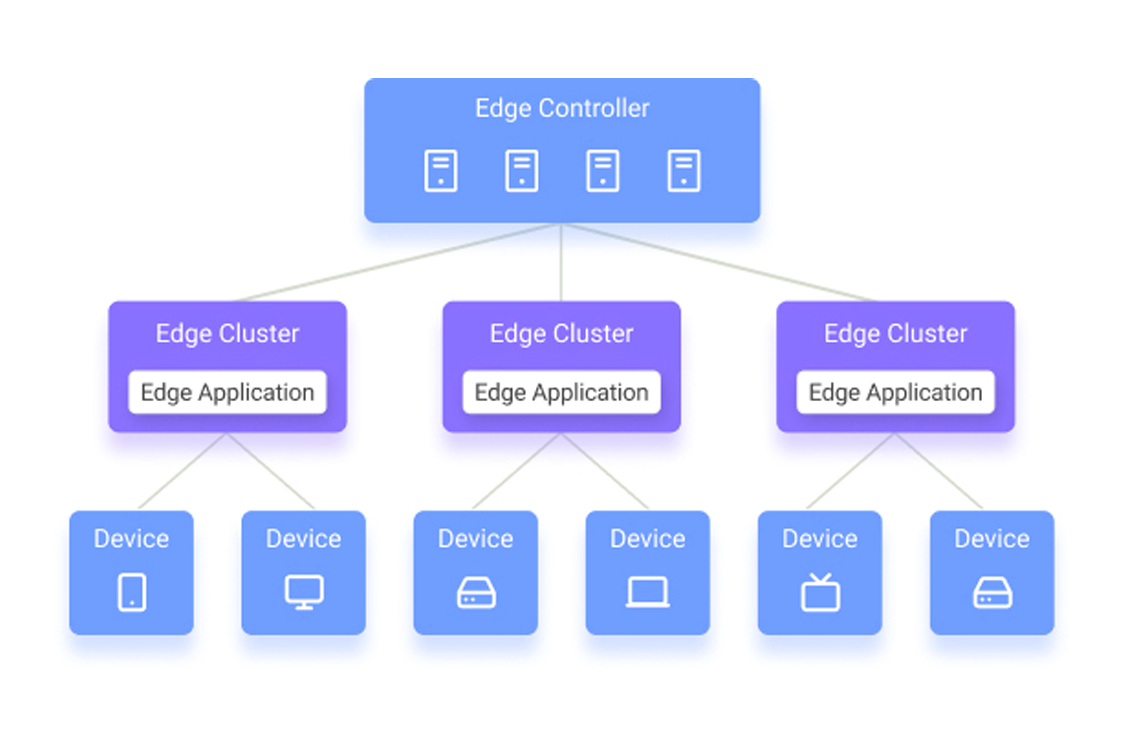
Edge computing describes computing that occurs near the source of data, rather than depending on cloud networks far from data access points to do all necessary computing. End devices refer to micro-servers, Edge-servers, computing devices, phones, laptops, and TVs, and include any device that shows the front end of data processing.
Meanwhile, computer vision is used to fulfill any tasks that would usually require the human eye. Edge computing is essential to computer vision operations because it improves response time, thus reducing bandwidth, and is more secure than most cloud computing platforms.
The Concept of Edge Computing
Why Is Edge Computing Useful?
What Are the Disadvantages of Edge Computing for AI Vision?
Involving all edge endpoints requires complex, distributed computing architectures. The need for integrated edge device management, monitoring, and configuration makes edge computing complex to implement and maintain.
Unlike cloud architecture, which is centralized around one common cloud, edge computing is distributed. The integration of multiple computing nodes requires networking and communication. The increased complexity requires fine balancing and optimization.
Compared to cloud-only architectures, edge computing enables large-scale systems with increased complexity. As a result, edge computing applications are more difficult and costly to build and maintain.
However, managed and automated infrastructure platforms help overcome the challenges of Edge Computing. Edge computing platforms enable organizations to utilize the benefits of both cloud and edge and to compute workloads in the most cost-efficient and scalable way.
What’s Next?
Due to the security and speed of edge computing regarding computer vision, it is an ever-growing industry and one of the major trends in IT. Therefore, more and more companies are implementing edge computing in combination with cloud services with their data because of its streamlined approach.
Related Products


Share this: